Data Encryption in the Cloud: What You Need to Know
In today’s digital world, where organizations increasingly rely on cloud services, protecting sensitive data has never been more critical.
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to safeguard data, ensuring that even if unauthorized individuals gain access, the information remains unreadable and secure.
In this post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of data encryption in the cloud, including its importance, the differences between encryption at rest and in transit, encryption methods used by major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP, and more.
We’ll also provide real-world examples and best practices to keep your data safe.

Why Encryption Is Essential for Cloud Security?
Encryption acts as a key shield to protect sensitive data in the cloud. Whether you’re storing financial records, personal information, or proprietary business data, encryption helps ensure that only authorized individuals can read or modify the information.
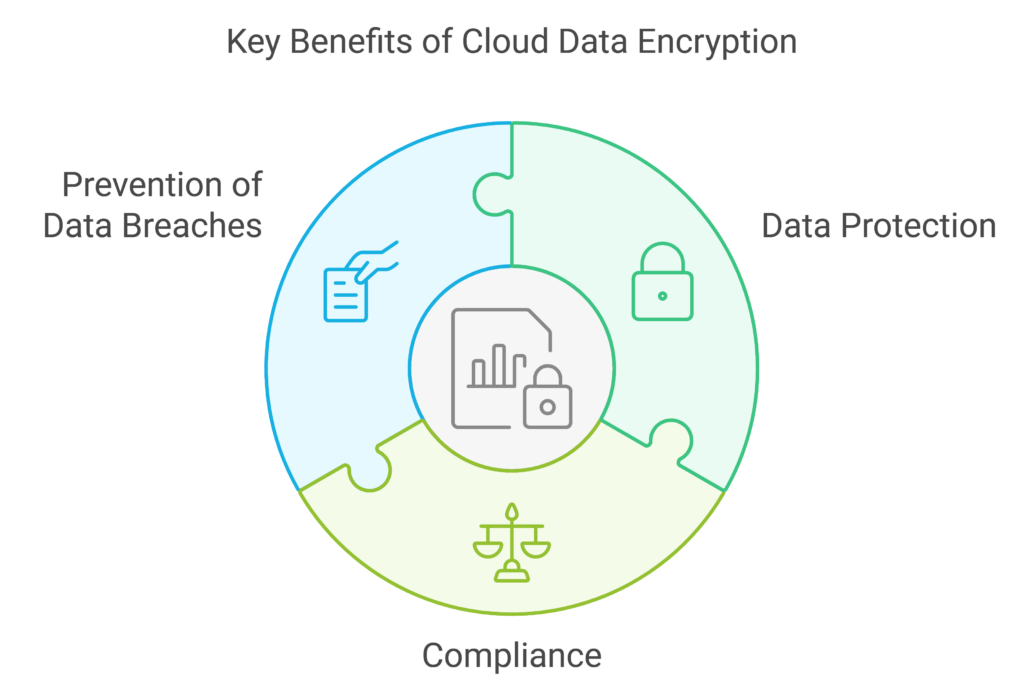
Key Benefits of Encryption:
- Data Protection: Even if attackers manage to access your data, encryption prevents them from understanding or using it.
- Compliance: Encryption helps meet regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, which require businesses to protect personal and financial information.
- Data Breaches: High-profile breaches, such as the Equifax data breach in 2017, could have been mitigated with better encryption practices, illustrating the crucial role of encryption in preventing unauthorized access.
Further reading on the importance of cloud security and encryption can be found in the NIST Cloud Security Standards and GDPR Encryption Guidelines.
Encryption at Rest vs. In Transit: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to protecting data in the cloud, there are two primary types of encryption:
Encryption at Rest
This is when data is encrypted while stored in databases, files, or any other type of storage system.
This ensures that even if physical drives or storage systems are stolen, the information remains secure.
- Example: Amazon S3 supports automatic server-side encryption for data at rest.
Encryption in Transit
This type of encryption protects data as it is transferred over the internet or internal networks.
It ensures that sensitive information is not intercepted and accessed during transmission between users and servers.
- Example: TLS/SSL encryption is used to secure data transmission on most modern websites.
Both types of encryption are essential for a complete data protection strategy. Some cloud services, such as Google Cloud and Azure, offer automatic encryption at rest, but encryption in transit may need to be configured manually.
Learn more about how these encryption types work from the Amazon S3 Encryption Documentation.
Encryption Methods in AWS, Azure, and GCP
Let’s look at how the top three cloud providers – AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud (GCP) – handle encryption.
1. AWS (Amazon Web Services)
AWS offers multiple encryption options for data at rest and in transit. Some of the key tools include:
- S3 Encryption: Protects data stored in Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (S3).
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS): Manages encryption keys in a secure and scalable way.
- Elastic Block Store (EBS) Encryption: Automatically encrypts data stored in Amazon EBS volumes.
AWS also supports client-side encryption, where data is encrypted before being uploaded to the cloud, offering a higher level of control for sensitive data.
- Official AWS documentation for encryption in AWS services.
2. Azure (Microsoft Azure)
Microsoft Azure provides several encryption tools:
- Azure Disk Encryption: Encrypts virtual machine disks using BitLocker for Windows or dm-crypt for Linux.
- Azure Key Vault: A centralized service for managing and securing encryption keys.
- Encryption for SQL Database: Transparent data encryption (TDE) protects data stored in Azure SQL databases.
Azure’s encryption offerings ensure both data at rest and in transit are secure, and it simplifies key management via Azure Key Vault.
- Learn more from the official Microsoft Azure Encryption Documentation.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud offers robust encryption options, including:
- Cloud KMS (Key Management Service): A cloud-hosted key management service that helps generate and store encryption keys.
- Cloud Storage Encryption: Automatically encrypts data at rest using AES-256 encryption.
- Customer-Supplied Encryption Keys (CSEK): Allows users to bring their own encryption keys to control access.
GCP also provides end-to-end encryption, ensuring data remains encrypted throughout its lifecycle.
- Visit the official Google Cloud Encryption Guide.
Best Practices for Key Management and Rotation
Effective encryption is more than just applying the right tools. Key management is critical for ensuring data remains secure, and there are several best practices you should follow:
- Centralize Key Management: Use a cloud-based key management service (like AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, or Google Cloud KMS) to store, manage, and rotate encryption keys.
- Implement Key Rotation Policies: Regularly rotate encryption keys to minimize the risk of exposure in the event of a breach.
- Access Control: Limit access to encryption keys to authorized personnel only, and make use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
For more information on encryption key management, check out the AWS Key Management Best Practices.
Client-Side vs. Server-Side Encryption
Understanding the difference between client-side and server-side encryption helps businesses determine the right approach based on their security requirements.
Client-Side Encryption
With client-side encryption, data is encrypted before it leaves the client’s environment and is uploaded to the cloud. This offers greater control and ensures that cloud providers or third parties never have access to unencrypted data.
- Use case: Organizations with strict regulatory requirements (like healthcare or finance) often prefer client-side encryption.
Server-Side Encryption
In this method, the cloud provider encrypts the data after it has been uploaded. This is simpler to implement since the provider manages both encryption and key management.
- Use case: Businesses that require scalability and ease of use may opt for server-side encryption since it simplifies data management.
Learn more about how server-side and client-side encryption differ on the Google Cloud Platform’s guide to encryption.
Regulatory Compliance and Cloud Encryption
Encryption plays a significant role in helping businesses comply with regulations and industry standards, especially when dealing with sensitive data. Here’s how encryption aids in compliance:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): In the EU, GDPR mandates that personal data be protected through encryption and other security measures. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): For businesses dealing with health information, HIPAA requires encryption to ensure patient confidentiality.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Payment card information must be encrypted to meet PCI DSS requirements.
These regulations often specify that businesses need to use strong encryption methods and maintain a secure key management process.
For more on encryption compliance, visit the GDPR guidelines.
Lessons from Data Breaches and Encryption Failures
Encryption doesn’t guarantee 100% protection if it’s not implemented correctly. Real-world data breaches demonstrate why encryption failures can lead to massive data leaks.
- Capital One Breach (2019): A misconfiguration in AWS led to the exposure of over 100 million credit applications. Better key management and encryption could have minimized the damage. Read more about the breach here.
- Equifax Breach (2017): In one of the largest breaches ever, sensitive data was exposed due to failure to patch vulnerabilities, underscoring the importance of encryption at all stages of data handling.
Conclusion: The Future of Cloud Encryption
As data continues to migrate to the cloud, encryption will remain a key defense against cyber threats. Following encryption best practices, staying compliant with regulations, and learning from past breaches will help businesses safeguard their data. Whether using AWS, Azure, or GCP, understanding how encryption works, managing encryption keys, and applying the right tools will keep your sensitive data secure in the cloud.
To stay updated on encryption standards and cloud security, follow the latest from:






