Cloud Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: A Comprehensive Guide
As organizations increasingly move their infrastructure and operations to the cloud, compliance with regulatory standards and frameworks becomes crucial.
Cloud compliance is essential for businesses across industries, especially those with sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government sectors.
This blog post will delve deep into why cloud compliance matters, explore the key compliance frameworks, discuss cloud provider compliance tools, and offer best practices for achieving compliance in cloud environments.
We’ll also touch on the shared responsibility model and the importance of industry-specific requirements, making this an authoritative guide to understanding and implementing cloud compliance strategies.
Why Cloud Compliance Matters?
In today’s digital landscape, businesses rely on cloud service providers (CSPs) to deliver scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. However, as data breaches and cyberattacks become more sophisticated, the regulatory landscape surrounding cloud security is growing more stringent. Compliance ensures that businesses protect sensitive data and adhere to industry regulations. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
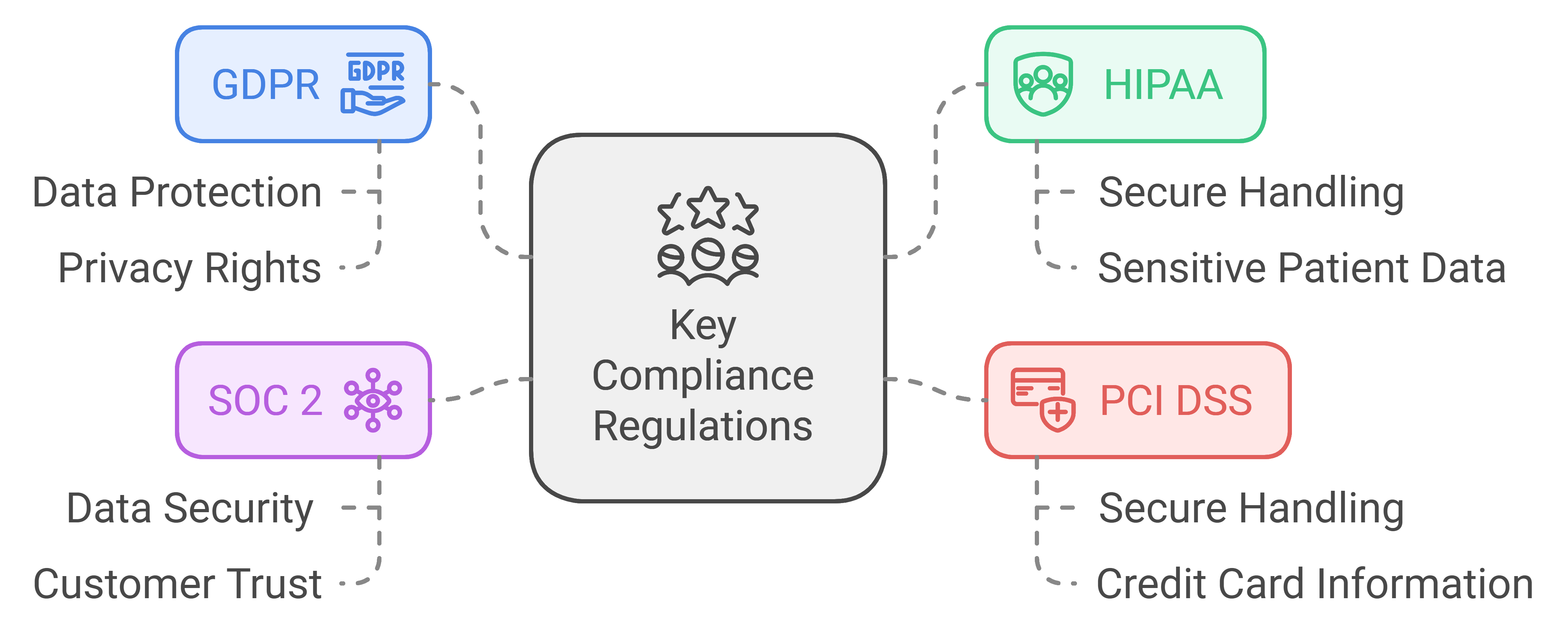
Some of the key regulations requiring compliance in cloud environments include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Governs data protection and privacy for all individuals in the EU and EEA (source).
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Mandates secure handling of sensitive patient data.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Ensures secure handling of credit card information.
- SOC 2: Focuses on the secure management of customer data.
Industries like healthcare and finance are subject to these stringent data protection regulations, and adhering to these regulations in the cloud environment is not optional. Let’s explore the critical compliance frameworks that businesses must adhere to in cloud environments.
Key Compliance Frameworks
Several compliance frameworks have been designed to address data protection, security, and privacy concerns in the cloud. Here are the most prominent ones:
1. ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It ensures that organizations manage sensitive data in a way that minimizes risks of data breaches. Compliance with ISO 27001 requires regular audits and adherence to strict protocols, making it a must for cloud service providers and their customers (source).
Why it matters in the cloud: Cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud must meet ISO 27001 standards to offer a secure environment. This framework is critical for any business that handles sensitive information.
2. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR is one of the most stringent and widely recognized regulations governing the use and protection of personal data for residents of the European Union. Any business that stores or processes the data of EU citizens must comply with GDPR, even if they operate outside of Europe (source).
Why GDPR matters in the cloud?: Cloud customers need assurance that their data will be processed in compliance with GDPR, and cloud providers must offer tools and services that help businesses maintain GDPR compliance. Providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer specific compliance features, such as data encryption and data residency options, to meet GDPR standards.
3. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of security standards aimed at protecting cardholder data during transactions. Companies handling payment information must adhere to this framework, ensuring secure storage, processing, and transmission of payment data.
Why PCI DSS matters in the cloud?: For businesses using cloud services to process payments, ensuring PCI DSS compliance is essential. Leading cloud providers offer tools to help businesses secure their cloud environments, such as encryption, monitoring, and audit logging, critical for maintaining PCI DSS compliance.
4. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA requires healthcare organizations and their partners to implement security measures that protect patient information. For organizations handling personal health information (PHI), HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable.
Why HIPAA matters in the cloud?: Many healthcare providers are moving to the cloud, so cloud service providers need to ensure they offer HIPAA-compliant environments. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all offer tools that help healthcare organizations secure and protect PHI.
5. SOC 2
SOC 2 focuses on the controls relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. It’s commonly used in the technology and SaaS industries to ensure cloud providers are handling data securely and responsibly.
Why SOC2 matters in the cloud?: SOC 2 compliance ensures that cloud providers have controls in place to protect against unauthorized access, misuse, or other cyber threats. It’s a crucial certification for businesses that provide cloud-based services and need to build trust with their customers.
Cloud Provider Compliance Tools
To meet these compliance standards, cloud providers offer native tools to assist their customers in auditing, managing, and ensuring compliance. Here’s a breakdown of some of the key tools provided by AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud:
1. AWS Artifact
AWS Artifact is a self-service portal that provides on-demand access to AWS compliance documentation, such as ISO certifications and SOC reports. It enables businesses to download these documents to demonstrate compliance to internal and external auditors.
- How it helps: AWS Artifact provides critical documentation that helps businesses stay compliant with frameworks such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and SOC 2.
2. Azure Compliance Manager
Azure Compliance Manager provides a dashboard that offers continuous assessments of your compliance posture based on real-time data. It includes built-in control mappings to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- How it helps: Azure Compliance Manager provides organizations with insights into compliance readiness, making it easier to track and maintain compliance in a cloud environment.
3. Google Cloud Compliance Reports
Google Cloud provides a comprehensive set of compliance reports that are regularly updated. These reports cover various standards like GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA, enabling businesses to demonstrate compliance when required.
- How it helps: With its extensive library of compliance reports, Google Cloud helps businesses quickly gather and present compliance evidence for audits or reviews.
Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Compliance
One key aspect of cloud compliance that businesses need to understand is the shared responsibility model. This model defines which security tasks are the responsibility of the cloud provider and which are the customer’s responsibility. Here you can find a more detailed article in our website for deep diving in the Shared Responsibility Model.
1. Cloud Provider Responsibilities:
The cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud, including the physical infrastructure, network security, and foundational services. This includes areas such as:
- Data center security: Ensuring physical security at data centers.
- Hardware maintenance: Maintaining secure servers, storage, and networking hardware.
- Encryption tools: Providing encryption capabilities and secure key management.
2. Customer Responsibilities:
The customer is responsible for securing what they do in the cloud. This includes:
- Data protection: Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Access control: Managing user permissions and roles.
- Application security: Ensuring the security of the applications they deploy in the cloud.
The shared responsibility model makes it clear that businesses cannot rely solely on the cloud provider to maintain compliance. They must take active steps to secure their workloads and data.
Not all of the services in Cloud Provider compliant with all the regulations, when designing and deploying solutions to the Public Cloud, based on regulatory compliance requirements, Cloud Services needs to be selected!
Industry-Specific Compliance Requirements
Different industries have their own unique compliance requirements. Here are a few examples:
1. Healthcare Industry: HIPAA Compliance
In the healthcare industry, protecting personal health information (PHI) is a top priority. HIPAA requires strict controls on how healthcare providers and their partners store and manage PHI. Cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer HIPAA-compliant services that include encryption, auditing, and identity access management (IAM).
2. Financial Services: FINRA and PCI DSS
Financial institutions must adhere to various compliance regulations, including FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority) for trading and securities, and PCI DSS for payment processing. These regulations require secure handling of financial data, encryption, and frequent audits. Cloud service providers offer specialized tools for encrypting, monitoring, and managing financial data securely.
3. Government Agencies: FISMA
Government agencies need to comply with FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act), which mandates specific security protocols for federal data. Cloud providers working with government agencies must provide FISMA-compliant services, including secure cloud infrastructure, strong identity management, and real-time auditing.
Best Practices for Achieving Compliance in Cloud Environments
Now that we’ve covered the importance of cloud compliance, key frameworks, and tools, let’s discuss some actionable best practices for staying compliant in the cloud:
1. Use Encryption Extensively
Data encryption is one of the most effective ways to ensure data security and compliance. Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit using advanced encryption standards like AES-256. Most cloud providers offer built-in encryption capabilities to help protect your data. For example, AWS provides options to encrypt data in Amazon S3, Relational Database Service (RDS), and other services using AWS Key Management Service (KMS), while Azure and Google Cloud also offer similar encryption tools.
2. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controlling who has access to your cloud environment is essential for compliance. Implement strong IAM policies to restrict access based on roles, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. Most cloud platforms offer robust IAM solutions. For example, AWS IAM, Azure Active Directory, and Google Cloud Identity allow you to define detailed permissions for users and services, ensuring the principle of least privilege is followed.
3. Regularly Audit and Monitor Cloud Activity
Maintaining continuous visibility into your cloud environment is essential for identifying and mitigating potential security risks. Use logging and monitoring tools like AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations Suite to track and record user activities. This not only helps you detect suspicious activity but also provides a valuable audit trail for compliance.
For example, AWS CloudTrail provides logs of all actions taken within your AWS account, ensuring you have a record of who did what, when, and where. Azure offers Azure Monitor for performance and availability monitoring and Azure Security Center for threat detection and compliance management. Google Cloud offers similar functionality with Operations Suite, which helps ensure ongoing compliance and security monitoring.
4. Stay Up-to-Date with Security Patches and Updates
One of the simplest but most crucial compliance practices is keeping your cloud infrastructure updated with the latest security patches. Cloud service providers release regular updates and patches to address vulnerabilities. Failing to apply these patches could leave your system exposed to threats, resulting in a potential breach and non-compliance.
Automation tools can help streamline this process. For instance, AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager helps automate the patching of EC2 instances. Azure Automation and Google Cloud’s OS Patch Management also provide similar automation services, ensuring your systems are up to date.
5. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing cloud resources. It’s a simple yet powerful way to strengthen security and ensure compliance with standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA. All major cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, offer MFA options.
6. Ensure Data Residency Compliance
Some regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR, require that data be stored within specific geographical locations. It’s important to choose data centers that meet these residency requirements to remain compliant. For instance, AWS provides customers with the flexibility to choose specific regions where their data is stored, and similar options are available from Azure and Google Cloud.
Data residency is a critical factor in ensuring compliance with regional laws, such as GDPR in the EU and China’s Cybersecurity Law, which imposes stringent requirements on the storage and transfer of personal data.
7. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits
To ensure continued compliance, conduct regular audits of your cloud environment. These audits should assess both the security controls provided by the cloud provider and the internal processes your organization follows to stay compliant. Many organizations choose to engage third-party auditors to validate compliance with frameworks such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, or PCI DSS.
For instance, cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer compliance checklists and built-in tools that help organizations maintain their compliance posture. Using these resources can help you stay ahead of regulatory requirements and maintain peace of mind.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Compliance
As cloud adoption grows, new trends and challenges are emerging in the cloud compliance landscape. Let’s briefly discuss some of these trends:
1. Multi-Cloud Compliance
More organizations are adopting multi-cloud strategies, utilizing services from multiple cloud providers simultaneously. This introduces a new challenge: ensuring compliance across different platforms. Multi-cloud governance tools, such as AWS Control Tower, Azure Arc, and Google Anthos, are evolving to help businesses maintain compliance in these complex environments by centralizing governance and compliance management across multiple cloud providers.
2. AI and Machine Learning Governance
With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), ensuring ethical and compliant use of these technologies is becoming more important. New regulations, such as the EU AI Act, are being introduced to ensure AI models are transparent, fair, and protect user privacy. Cloud platforms offer services like AWS SageMaker, Azure Machine Learning, and Google AI to help organizations implement AI governance frameworks that meet these emerging regulatory requirements.
3. Zero Trust Security Models
The Zero Trust model is gaining traction in cloud environments. It requires continuous verification of users and devices, regardless of their location, before granting access to resources. Implementing a Zero Trust architecture can help businesses meet modern compliance requirements by reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Leading cloud providers are integrating Zero Trust principles into their platforms to support compliance. For example, Google BeyondCorp enables Zero Trust security models, while Azure Conditional Access and AWS IAM provide similar functionality.
Conclusion
Cloud compliance is a critical aspect of operating in today’s digital landscape. From understanding key compliance frameworks like ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, to leveraging cloud provider tools such as AWS Artifact, Azure Compliance Manager, and Google Cloud Compliance Reports, businesses have a wide range of resources available to meet their compliance needs.
However, compliance in the cloud requires a proactive approach. By following best practices—such as using encryption, implementing IAM policies, and conducting regular audits—organizations can stay ahead of compliance requirements and ensure the security of their data.
As cloud technology evolves, it’s important to stay aware of emerging trends like multi-cloud compliance, AI governance, and the shift to Zero Trust security models. The regulatory landscape is continuously changing, and organizations need to adapt to remain compliant in a cloud-first world.
By understanding the shared responsibility model, adhering to industry-specific regulations, and keeping an eye on emerging trends, organizations can ensure they remain compliant in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.