Serverless computing has revolutionized the way developers build and deploy applications. DigitalOcean Functions, a powerful serverless platform, allows developers to run code without managing servers. This approach simplifies the development process and reduces operational costs, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
This article will guide readers through the process of deploying serverless applications using DigitalOcean Functions. It will cover the basics of DigitalOcean’s serverless platform, setting up a development environment, writing a first serverless function, and deploying and testing the function. By the end, readers will have the knowledge to start using DigitalOcean Functions for their own projects.
Understanding DigitalOcean Functions
What are serverless functions?
Serverless functions are blocks of code that run on demand without the need to manage any infrastructure. They form the basis of serverless architecture, a design approach for web applications and services that doesn’t rely on managing backend infrastructure. In this model, cloud providers like DigitalOcean handle the provisioning, management, and scaling of backend servers and components required to host applications.
DigitalOcean Functions is a function as a service (FaaS) platform that allows developers to deploy code capable of performing the same tasks as a traditional API without setting up a server to manage requests. These functions only run in response to events or requests, making them cost-effective for components with fluctuating amounts of requests.
Benefits of using DigitalOcean Functions
DigitalOcean Functions offers several advantages to developers and businesses:
Enhanced developer productivity: Since DigitalOcean manages resource provisioning and scaling, developers can focus more on improving their code rather than dealing with infrastructure concerns.
Cost savings: By eliminating the need to maintain idle servers, users only pay for resources when they are actively running. This pay-as-you-go model can lead to significant cost reductions.
Automatic scaling: DigitalOcean handles the scaling of infrastructural components based on demand, removing the need for manual intervention.
Faster time to market: Developers can write functions in their preferred language and deploy them easily without having to learn complex infrastructure-oriented concepts like containers and Kubernetes.
Seamless database integration: DigitalOcean Functions can be easily integrated with Managed Databases for MySQL, Redis, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, allowing for efficient data management within applications.
Supported runtimes and languages
DigitalOcean Functions supports a variety of popular programming languages and runtimes, catering to different developer preferences and project requirements. The platform currently offers eight different runtimes across four programming languages:
Go: versions 1.17 and 1.20
Node.js: versions 14 and 18
PHP: versions 8.0 and 8.2
Python: versions 3.9 and 3.11
This range of options allows developers to work with their preferred language and take advantage of specific version features. DigitalOcean takes care of applying patches and updates to ensure a stable and secure execution environment.
To view the list of supported runtimes, you can use the command
doctl serverless status --languages in your terminal.
By offering these diverse runtimes and languages, DigitalOcean Functions enables developers to build and extend their applications easily without the need to learn new frameworks or languages, further streamlining the development process and enhancing productivity.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
To begin working with DigitalOcean Functions, developers need to set up their development environment. This process involves installing the necessary tools, configuring authentication, and creating a project.
Installing doctl CLI
The first step is to install the DigitalOcean Command Line Interface (CLI) tool, known as doctl. This versatile tool allows developers to interact with DigitalOcean services, including Functions, from the command line.
For macOS users, the easiest way to install doctl is through Homebrew. Simply run the following command in the terminal:
brew install doctl
Ubuntu and other supported Linux distributions can use Snap to install doctl:
sudo snap install doctl
Windows users can download the appropriate archive from the doctl GitHub Releases page and extract the binary to a dedicated directory.
After installation, it’s recommended to enable shell auto-completion for doctl. This feature allows for faster command input by automatically filling in partial commands when the TAB key is pressed.
Configuring authentication
Once doctl is installed, the next step is to authenticate it with your DigitalOcean account. This process involves creating an API token and using it to grant doctl access to your account.
To create an API token:
Log in to your DigitalOcean account and navigate to the API section in the control panel.
Generate a new token with read and write access.
Copy the token string and keep it secure, as it will only be displayed once.
With the token in hand, run the following command to authenticate doctl:
doctl auth init
When prompted, enter your API token. This process creates the necessary configuration files to store your credentials securely.
Creating a DigitalOcean Functions project
After setting up doctl and authenticating your account, you’re ready to create a DigitalOcean Functions project. The first step is to install the serverless extension for doctl:
doctl serverless install
Next, create a namespace to organize your serverless functions:
doctl serverless namespaces create --label myproject --region nyc1
Replace “myproject” with your desired namespace name and choose an appropriate/closest region to you or end API users.
Regional Availability | DigitalOcean Documentation
| DigitalOcean Datacenter | Region | Slug |
|---|---|---|
| NYC1 | New York City, United States | nyc1 |
| NYC2 | New York City, United States | nyc2 |
| NYC3 | New York City, United States | nyc3 |
| AMS3 | Amsterdam, the Netherlands | ams3 |
| SFO2 | San Francisco, United States | sfo2 |
| SFO3 | San Francisco, United States | sfo3 |
| SGP1 | Singapore | sgp1 |
| LON1 | London, United Kingdom | lon1 |
| FRA1 | Frankfurt, Germany | fra1 |
| TOR1 | Toronto, Canada | tor1 |
| BLR1 | Bangalore, India | blr1 |
| SYD1 | Sydney, Australia | syd1 |
Finally, connect to your newly created namespace:
doctl serverless connect
With these steps completed, your development environment is now set up for working with DigitalOcean Functions. You can start creating and deploying serverless applications, leveraging the power of DigitalOcean’s infrastructure without managing servers directly.
Remember to keep your doctl installation updated to access the latest features and improvements for working with DigitalOcean Functions and other serverless capabilities.
Writing Your First Serverless Function
Choosing a runtime
DigitalOcean Functions supports various programming languages and runtimes, giving developers flexibility in their serverless applications. The platform offers eight different runtimes across four popular programming languages:
Go: versions 1.17 and 1.20
Node.js: versions 14 and 18
PHP: versions 8.0 and 8.2
Python: versions 3.9 and 3.11
To specify the desired runtime and version, use the runtime key in your project.yml file or select it from the Runtime dropdown when creating a function through the control panel. This allows you to leverage the language and version that best suits your project’s needs.
Creating the Initial Version of the Function
You can create the initial boilerplate of the function with the help of following command. It will create basic project folder structure and project settings file.
doctl serverless init --language python test-project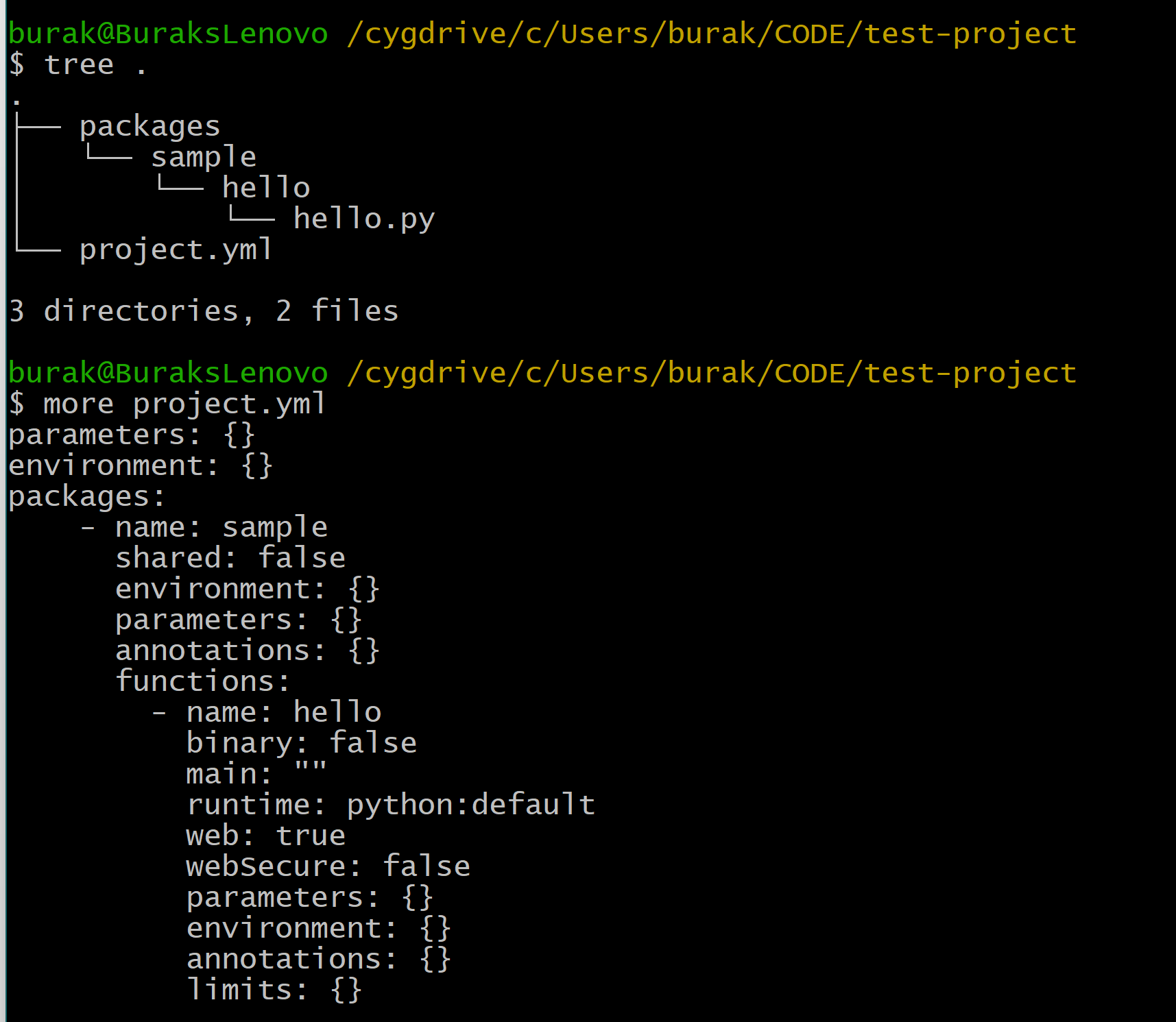
Deploying and Testing Your Function
After writing your serverless function, the next step is to deploy and test it using DigitalOcean Functions. This process involves using the doctl command-line tool, accessing your function’s URL, and monitoring its performance.
Using doctl to deploy
To deploy your function, you can use the doctl serverless deploy command. This command uploads the contents of your functions project to your serverless namespace for testing. The project must be organized in the structure expected by an App Platform Functions component. If you’re unsure about the proper organization, you can use the doctl serverless init command to create a correctly structured directory for your work.
When you’re ready to deploy, simply run:
doctl serverless deploy
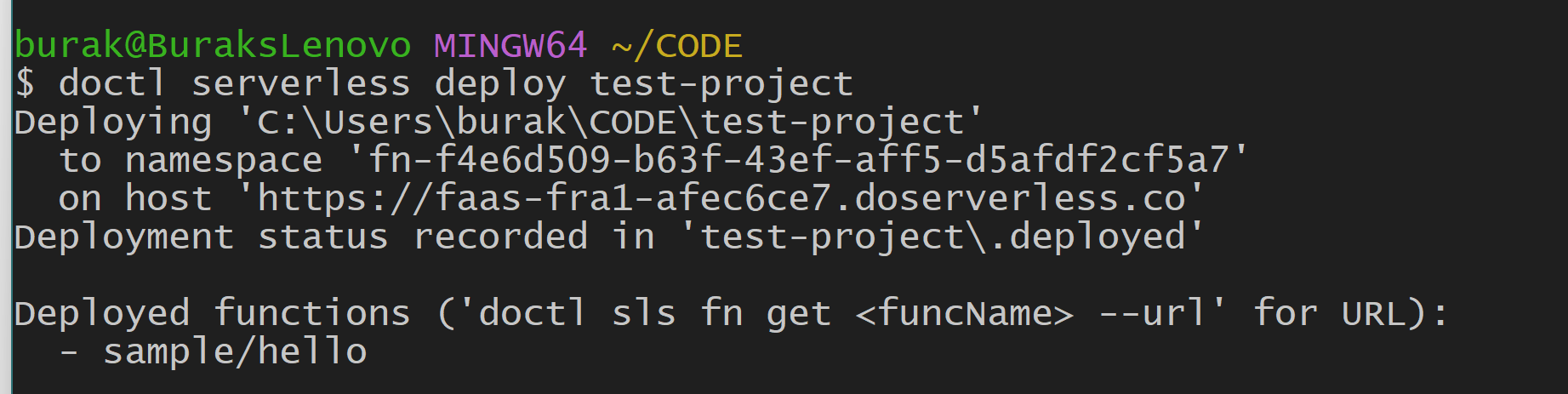
This command will package your function and deploy it to DigitalOcean Functions. Once deployed, you can use the doctl serverless functions list command to view your deployed functions. The output will show you the names of your functions and their associated packages.
Accessing your function’s URL
After deployment, each function receives a public URL (anybody can access it if they know!!!) that you can use to invoke it. To retrieve this URL, use the following command:
doctl serverless functions get <function_name>

Replace <function_name> with the name of your function. This command will return a URL similar to:
https://faas-nyc1-<random-string>.dofunction.dev/api/<namespace>/<function_name>
You can use this URL to invoke your function directly from a web browser or through API calls in your application.

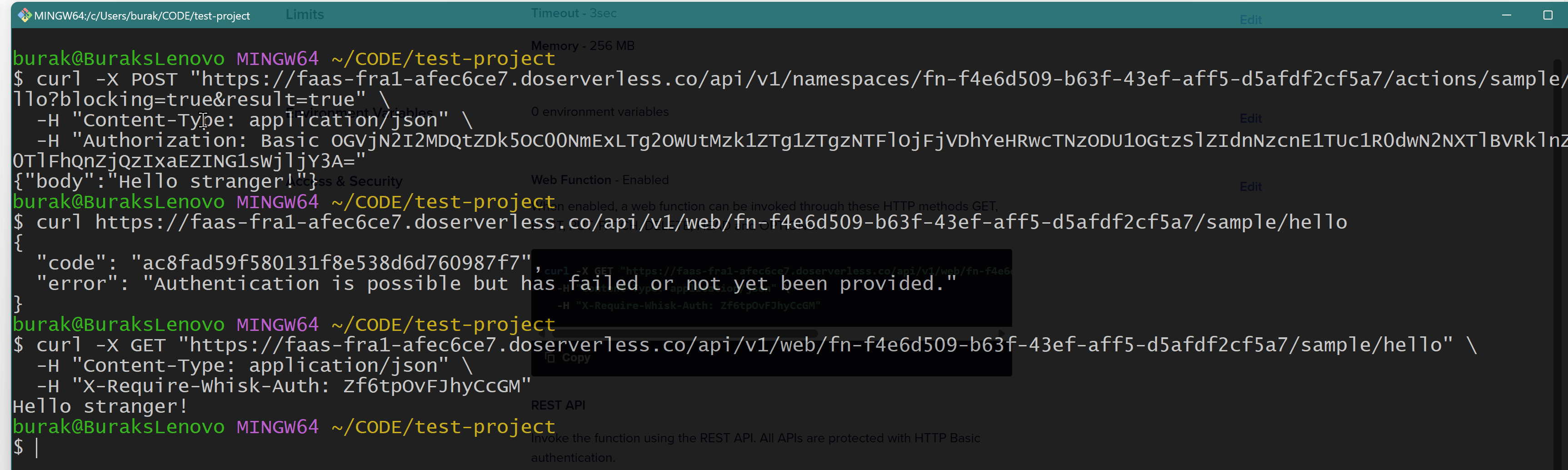
If you want to add Basic Authentication to your function you have to go to the DigitalOcean console and change it in the security Tab.
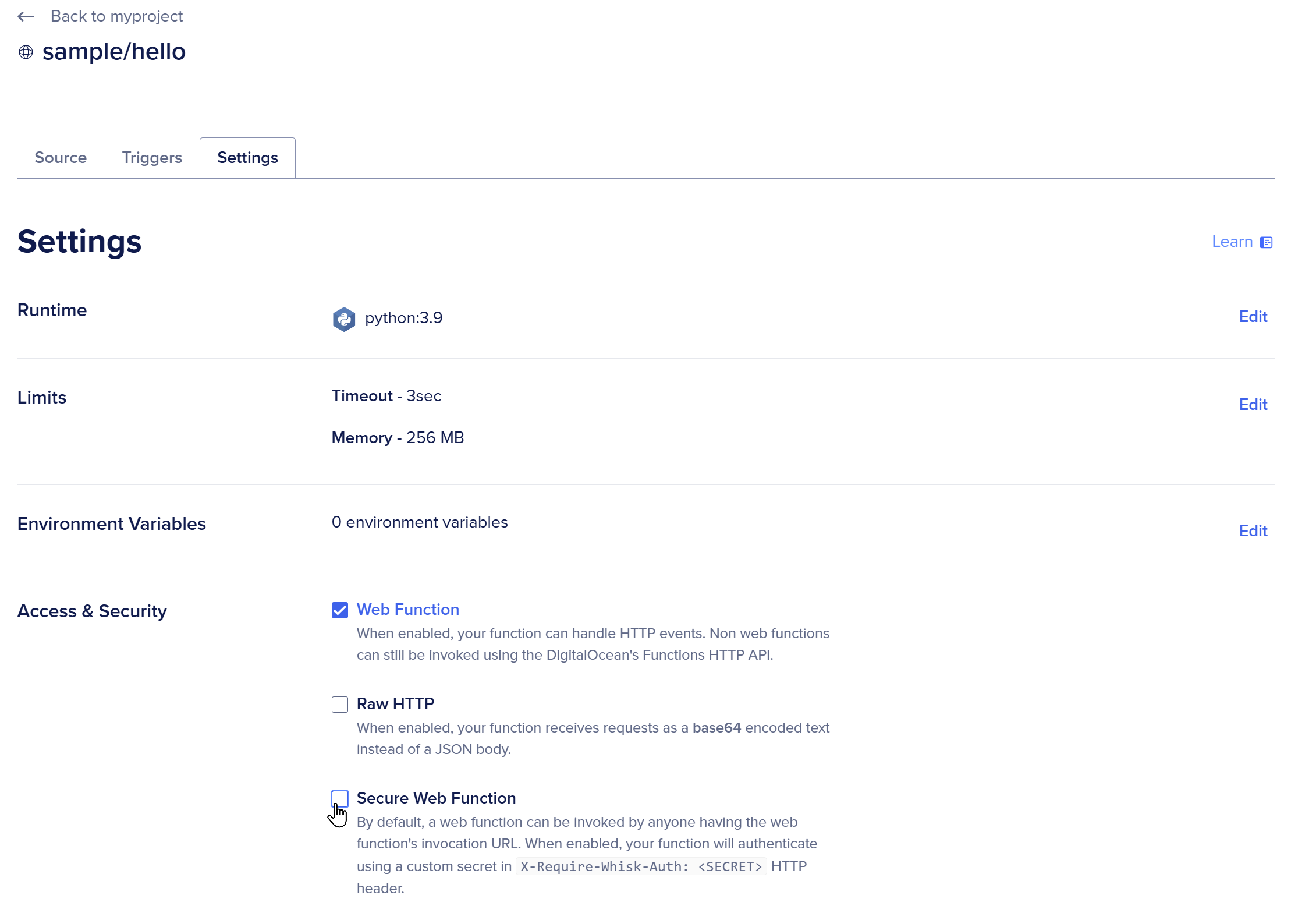
And after enabling Secure Authentication, you have to provide basic Auth header, the function will not be accessible from internet without authentication!
Monitoring and debugging
Monitoring and debugging are crucial for ensuring your serverless applications operate smoothly. DigitalOcean Functions provides several tools to help you monitor your functions’ performance and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
To view the logs for your function, you can use the doctl serverless activations logs command. By default, this command shows the logs from the most recent activation, but you can use the --limit flag to view more:
doctl serverless activations logs --limit 3
This command returns a header with the activation ID, status, date and time, and function version information, followed by the actual logged output.
For more detailed information about a specific activation, you can use the activation ID to retrieve the full activation record:
doctl serverless activations get <activation_id>
This command returns a JSON object containing logs, response status, response body, and other details that can be useful for debugging.
In addition to command-line tools, you can also use the DigitalOcean control panel to monitor your functions. The control panel provides a basic text editor for single-file functions and the ability to run functions, pass in parameters, and view output and logs.
When debugging, it’s important to be aware of common errors in serverless applications. These can include rate limit errors, incorrect invocation or event payloads, resource allocation issues, and security configuration errors. Proper error handling and logging can help you identify and address these issues quickly.
By leveraging these deployment, testing, and monitoring tools, you can ensure your DigitalOcean Functions are running efficiently and effectively. Remember to regularly review your functions’ performance and logs to maintain optimal operation of your serverless applications.
Conclusion
Serverless computing has caused a revolution in app development, and DigitalOcean Functions offers a user-friendly way to jump into this world. By following the steps outlined in this article, developers can easily set up their environment, write functions, and deploy them without the hassle of managing servers. This approach not only streamlines the development process but also has a significant impact on cost reduction and scalability.
As you dive into serverless development with DigitalOcean Functions, remember that practice makes perfect. Keep exploring new ways to use functions, experiment with different runtimes, and don’t be afraid to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
To kickstart your serverless journey, get your $200 credit from DigitalOcean and start building your dream app today. With the right tools and mindset, you’ll soon be creating powerful, scalable applications that can adapt to any challenge.
FAQs
How are serverless functions deployed?
Serverless functions are deployed by writing a function in a preferred programming language and then sending it to a serverless provider. This function can then be invoked like any API using HTTP methods.How can the deployment of a serverless application be automated?
To automate the deployment of a serverless application, one can use doctl cli along with a continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) system. This deployment pipeline automates the sequence of steps necessary to release a new version of the serverless application.What distinguishes DigitalOcean Functions from DigitalOcean App Platform?
DigitalOcean App Platform is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that allows developers to publish code directly to DigitalOcean servers without managing the underlying infrastructure. In contrast, DigitalOcean Functions are blocks of code that execute on demand without the need to handle any infrastructure, focusing solely on the code execution.How do serverless functions operate?
Serverless functions operate by allowing developers to write back-end code without the need to manage a back-end infrastructure. Developers write functions in their chosen language, deploy these to a serverless provider, and execute them via standard HTTP methods, treating them similarly to APIs.