What is Hybrid Cloud? Best of Both Worlds
Imagine having both a kitchen at home and occasionally eating at restaurants.
Sometimes you cook privately, other times you enjoy public dining.
That’s hybrid cloud – using both private and public clouds together!

How Hybrid Cloud Works
Easy explanation for you;
Hybrid cloud combines elements of both public cloud services (like AWS, Azure o Google Cloud) and private cloud infrastructure (typically hosted on-premises or in a dedicated data center).
- Hybrid cloud integrates private and public clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This setup gives businesses flexibility, allowing them to keep sensitive data in their private cloud while utilizing the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud services for less sensitive tasks.
You can keep your data and applications where it is relevant, compliant and working better for your business.
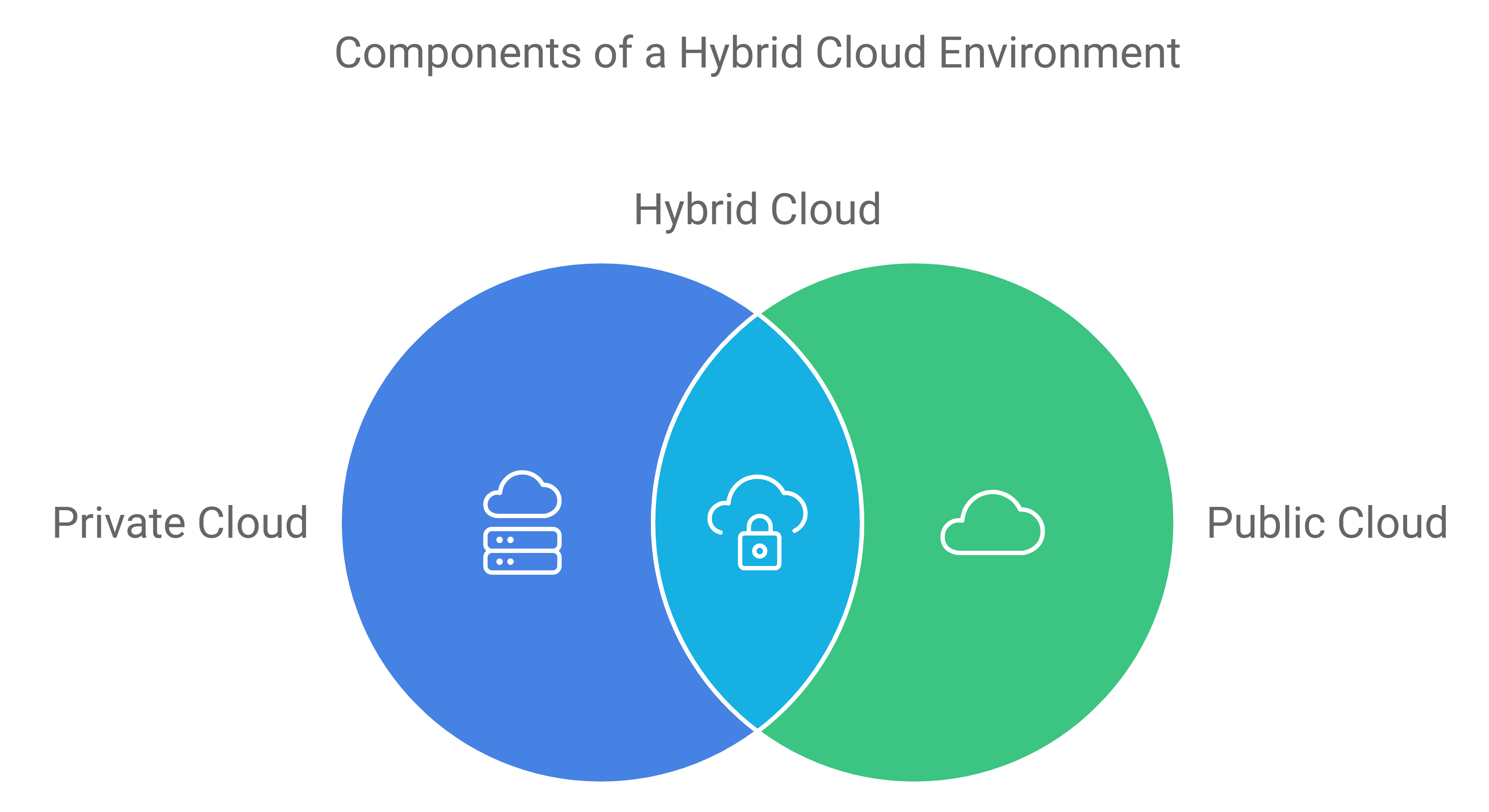
Breakdown of Hybrid Cloud Environment
- Architecture: Typically, a hybrid cloud environment includes:
- Private Cloud: Infrastructure dedicated solely to one organization, providing control and security.
- Public Cloud: Services offered by third-party providers, accessible via the internet, offering scalability and diverse services like computing power, storage, and applications. (Likely AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Ali Baba etc)
- Integration: The key challenge is seamless integration between the two environments. This often involves:
- Connectivity: Secure network connections (like VPNs or dedicated lines) to link private and public clouds.
- Management: Unified management tools to oversee and coordinate resources across both environments.
- Data Consistency: Ensuring data remains consistent and accessible across both clouds as needed.
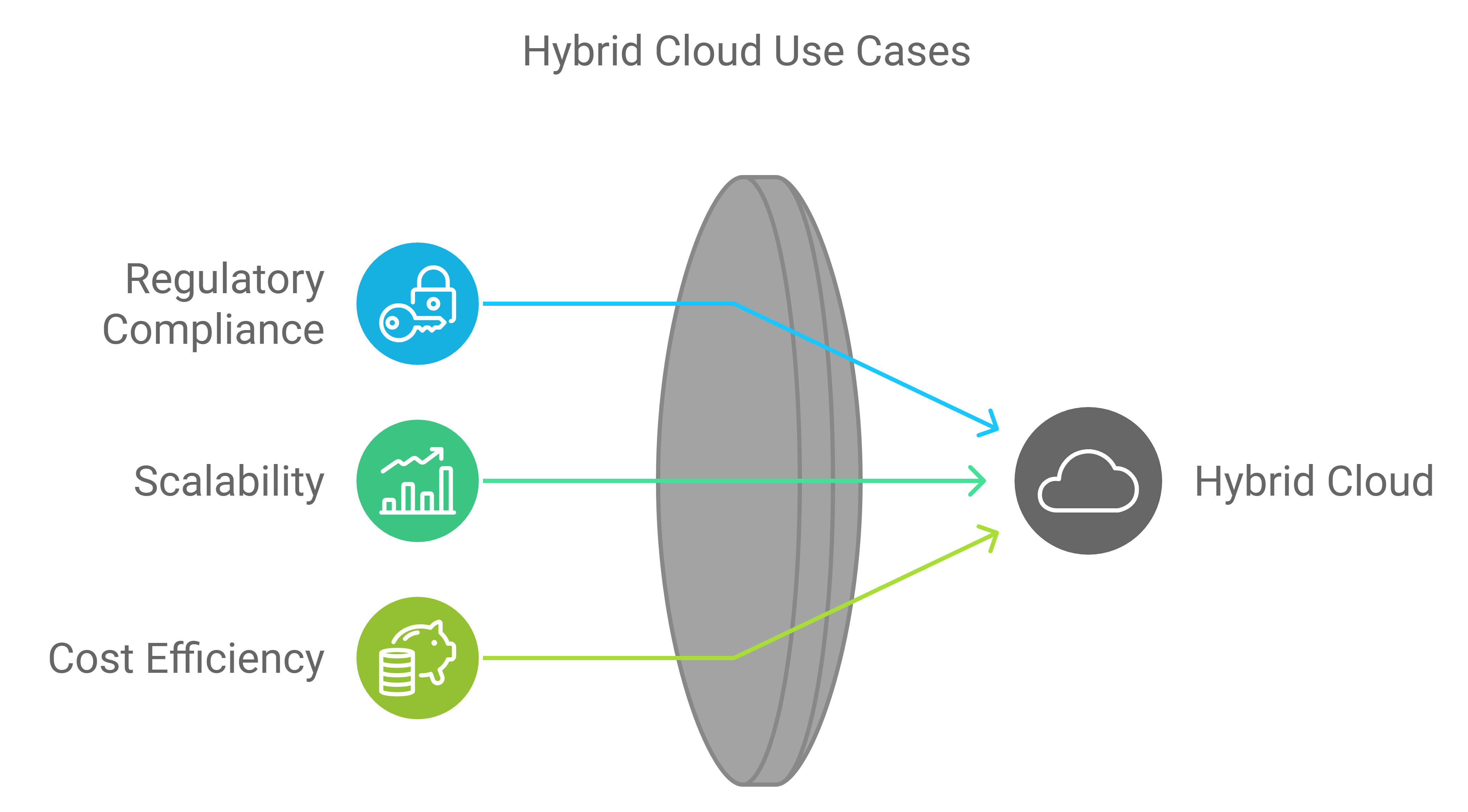
- Use Cases: Hybrid cloud is useful for:
- Regulatory Compliance: Keeping sensitive data in a compliant private cloud environment.
- Scalability: Using public cloud resources for peak demand periods or specific projects.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizing costs by balancing resource usage between private and public clouds.
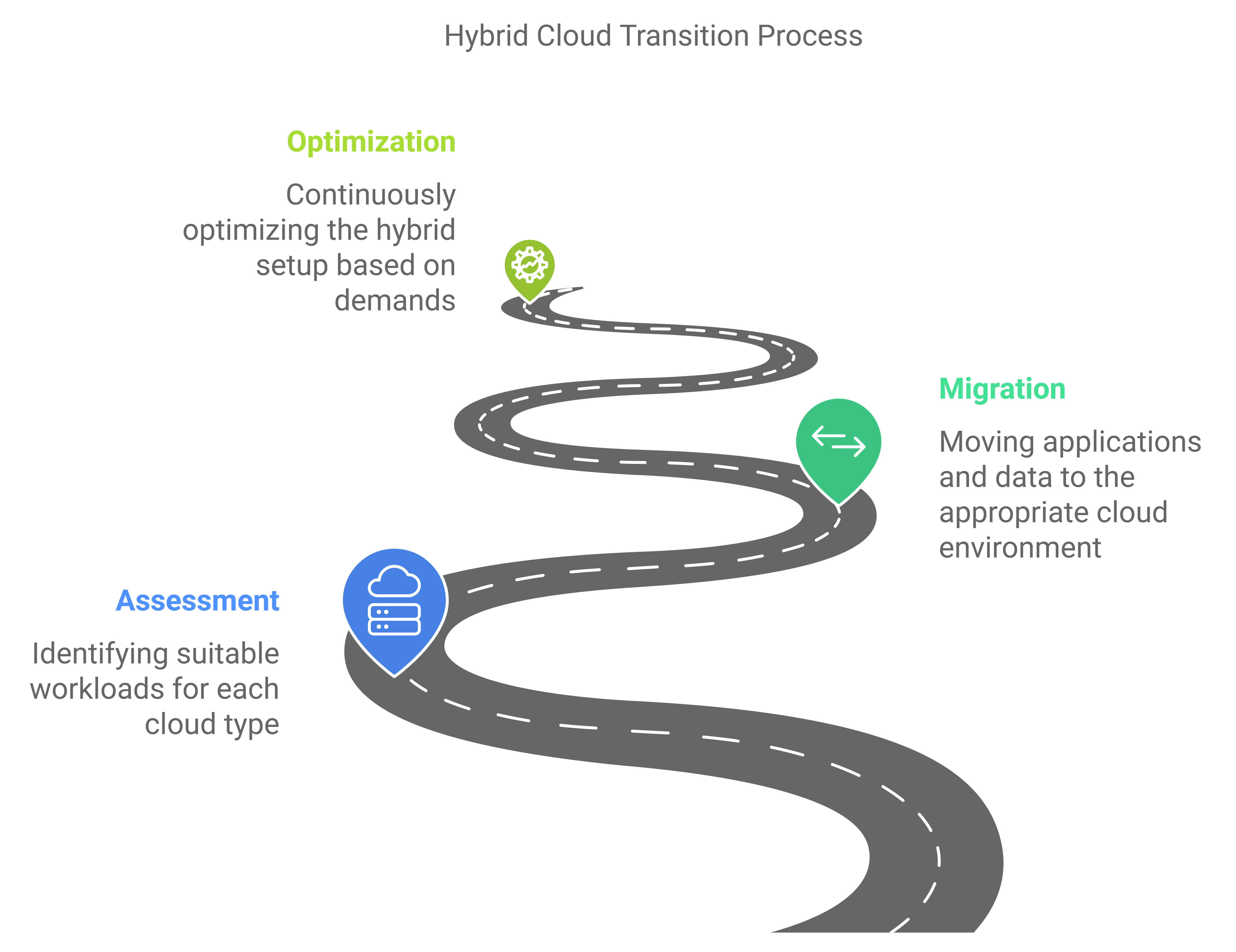
- Transition and Adoption: Organizations typically transition to hybrid cloud gradually:
- Assessment: Identifying which workloads are suitable for each cloud type based on security, performance, and regulatory requirements.
- Migration: Moving applications and data to the appropriate cloud environment, often using tools and strategies to minimize disruption.
- Optimization: Continuously optimizing the hybrid setup based on workload demands and cost considerations.
Real-Life Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
A retail store might:
- Store customer data on a private cloud for better security
- Run their website on a public cloud for scalability and flexibility
- Connect both systems seamlessly to ensure smooth operations
Consider a healthcare provider:
- Store patient records on a private cloud for compliance and data security.
- Run patient-facing appointment booking services on a public cloud to handle large user loads efficiently.
- Connect both systems seamlessly so that patient data can be accessed by doctors securely while using scalable public cloud tools for easier appointment management.
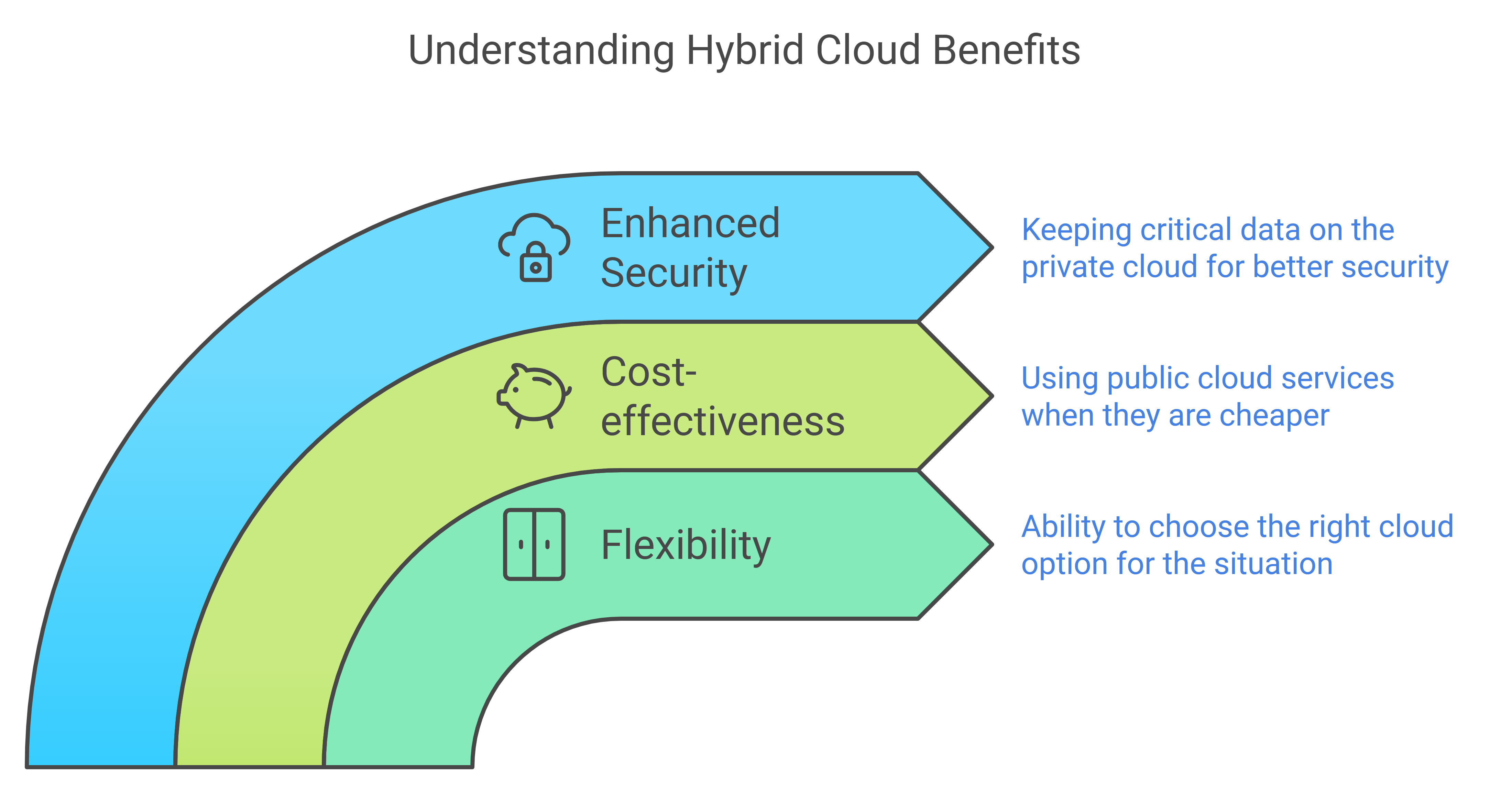
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Flexibility: Like having both casual and formal clothes, choose the right option for the situation.
- Cost-effective: Use public cloud services when they are cheaper and save on costs.
- Enhanced security: Keep critical data on the private cloud where it’s more secure.
- Scalability without Compromise: When your needs grow, hybrid cloud enables you to scale using the public cloud. For example, a retail store can use the private cloud for inventory management but use public cloud servers during major sales events like Black Friday, ensuring their website runs smoothly.
Comparison with Other Cloud Service Models
To understand why hybrid cloud stands out, let’s compare it to other cloud service models:
Public Cloud
Public cloud services, like those offered by AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, provide infrastructure and services that are available to the general public. These are cost-effective and highly scalable, making them perfect for less sensitive workloads. However, data privacy and security can be a concern, as resources are shared with other users. Here you can read our other post regarding Public Cloud.
Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to cloud infrastructure that is dedicated entirely to a single organization. It offers enhanced control, privacy, and security, similar to hosting your own data center. However, private clouds can be costly, as they require significant investment in hardware and maintenance, making them less flexible compared to public cloud. Here you can read our other post regarding Private Cloud
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is a mix of both. It allows organizations to keep sensitive data and critical workloads on a private cloud while leveraging the cost-efficiency and scalability of the public cloud for less critical tasks. This means you get the best of both worlds—flexibility, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Why Hybrid Cloud is a Smart Choice
Hybrid cloud provides the best of both worlds. It offers flexibility, cost savings, and better security. You get to choose the right environment for the right task, just like deciding between cooking at home or dining out. By blending the benefits of both public and private clouds, hybrid cloud gives you a tailored solution, perfect for balancing security, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
Summary
Whether you are a small business looking to cut costs, or a large enterprise wanting to maintain control over critical data, hybrid cloud offers a mixed cloud environment that can adapt as your needs change.
It’s about making cloud computing work for you, there is no one-rule or one size fits for all, leveraging the strengths of both public and private clouds to achieve a more powerful and flexible infrastructure.